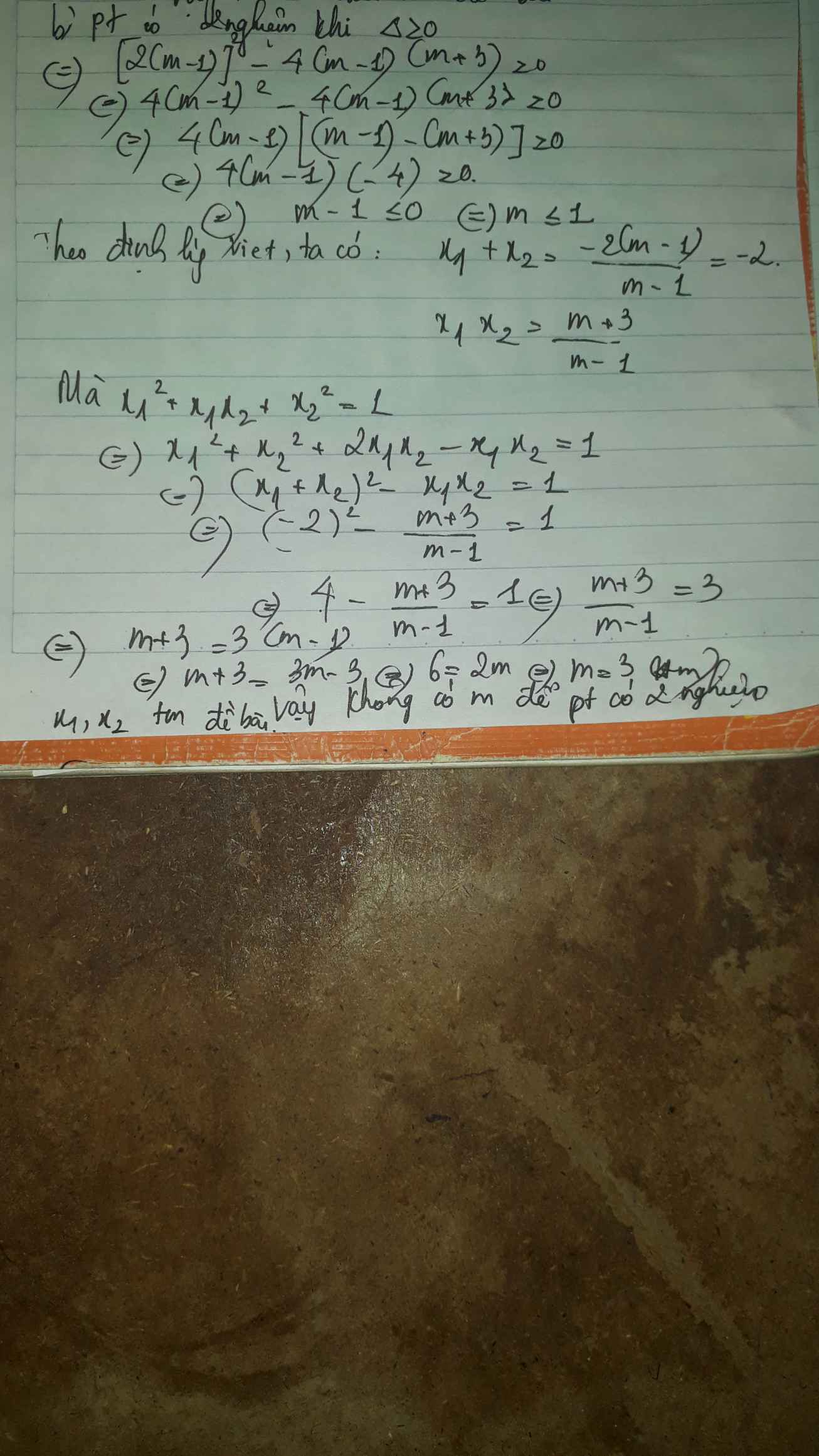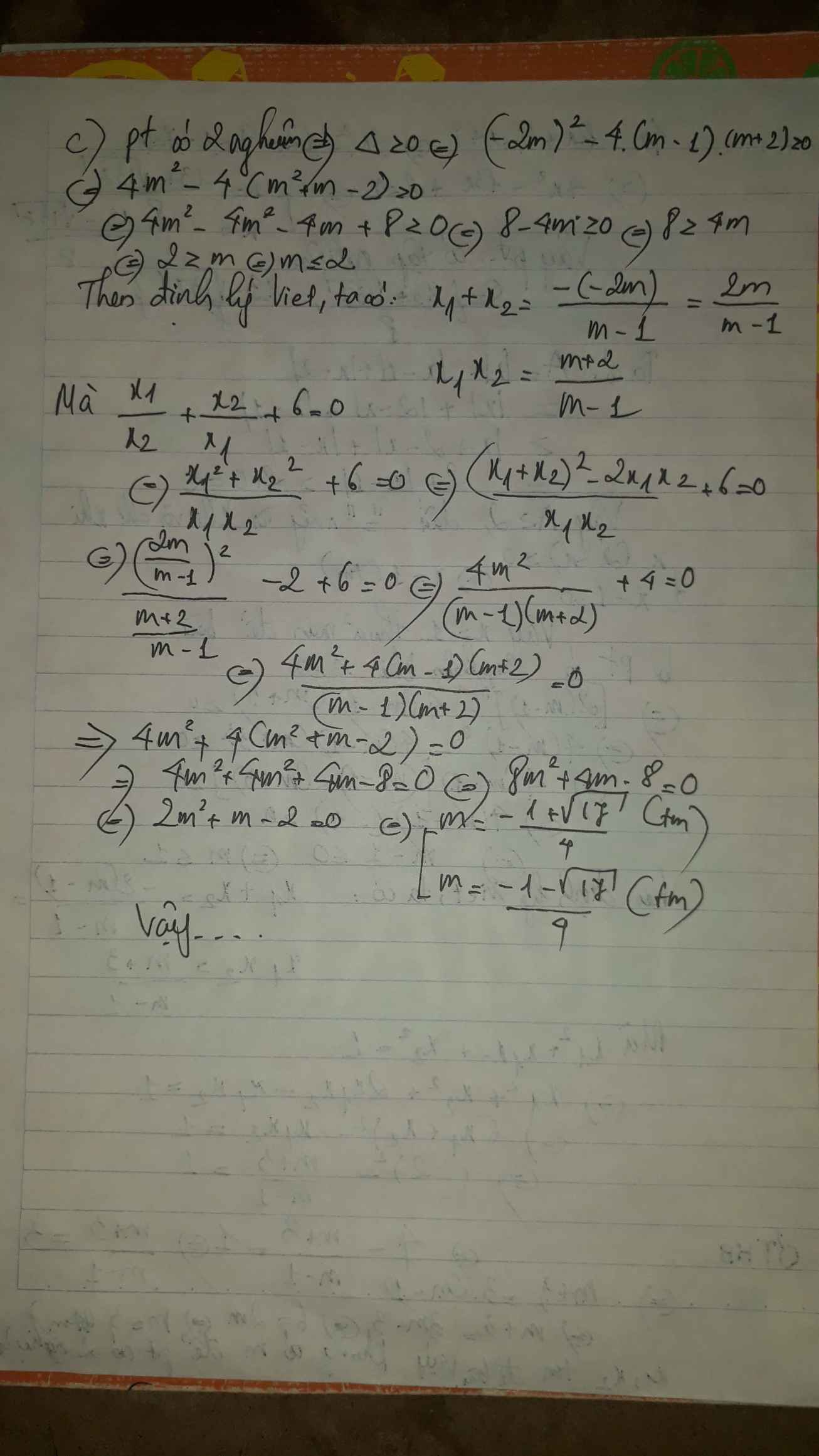Gọi x1, x2 là nghiệm của phương trình x2+2x-4=0. Hãy lập phương trình bậc hai có 2 nghiệm là:
a) x1+2 và x2+2
b) \(\dfrac{1}{x_1+1}\) và \(\dfrac{1}{x_2+1}\)
c) \(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}\)và \(\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}\)
d) \(x^2_1\)+\(x^2_2\) và \(x_1\)+\(x_2\)
Mọi người giúp mình với. Cần gấp trước 19h15 hôm nay, mình cảm ơn trước ạ.